Search Hospitals
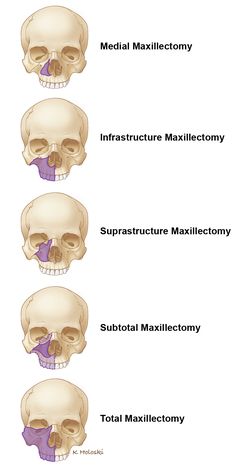
Maxillectomy
Medial maxillectomy refers to surgical re- section of the medial and superomedial walls of the maxillary antrum.
Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery specializes in surgery of the face, mouth, and jaws. It is an internationally recognized surgical specialty.
MC - Metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders and mental retardation. Kahler SG(1), Fahey MC. The metabolic and anatomical substrate of most forms of mental retardation is not known.

MC - Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology.
Medical Oncology & Clinical Hematology
Clinical Hematology and Oncology: Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment.

Multiple disorders
Disorder that is characterized by the presence of two or more distinct and complex identities.
Multispecialities
Multi- Specialty Hospital is the hospital which has all the different branches of Medicine and surgery under one roof.
Nanotechnology
Encompassing nanoscale science, engineering, and technology, nanotechnology involves imaging, measuring, modeling, and manipulating matter at this length scale.

Nasya Treatment
Nasya is a therapeutic treatment for the nose, throat, sinuses and head.

Naturopathy
Naturopathy is a system of man building in harmony with the constructive principles of Nature on physical, mental, moral and spiritual planes of living.
Neonatology
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that consists of the medical care of newborn infants, especially the ill or premature newborn.
Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty of medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns itself with the kidneys: the study of normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy.
Neurology
Neurology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle.

Neuro-ophthalmology & Electrophysiology
Neuro-ophthalmology is an ophthalmic subspeciality that addresses the relationship between the eye and the brain,
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery, or neurological surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, surgical treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebrovascular system.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease.

Ocular Prosthesis
An ocular prosthesis, artificial eye or glass eye is a type of craniofacial prosthesis that replaces an absent natural eye following an enucleation, evisceration, or orbital exenteration.

Oculoplasty & Orbit Surgery
Orbit refers to the eye-socket (the cavity in the skull that holds the eye) and the surrounding structures.
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ?????, meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass" and the word ?????, meaning "study".
.jpg)
Opthalmology
Ophthalmology is a branch of medicine and surgery which deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a specialist in ophthalmology. The credentials include a degree in medicine, followed by additional four to five years of ophthalmology residency training. Ophthalmology residency training programs may require a one-year pre-residency training in internal medicine, pediatrics, or general surgery.

Organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location.
Orthopaedic
Orthopaedic surgery is a specialty dealing with acute injuries, congenital and acquired disorders and chronic arthritic or overuse conditions of the bones, joints and their associated soft tissues, including ligaments, nerves and muscles.

Outpatient care services
Outpatient care is a broad category that generally includes all services provided to patients that are not given ...

Pain & Palliative care
Palliative care (pronounced pal-lee-uh-tiv) is specialized medical care for people with serious illnesses.
Pain Managment
Pain management can be simple or complex, depending on the cause of the pain.
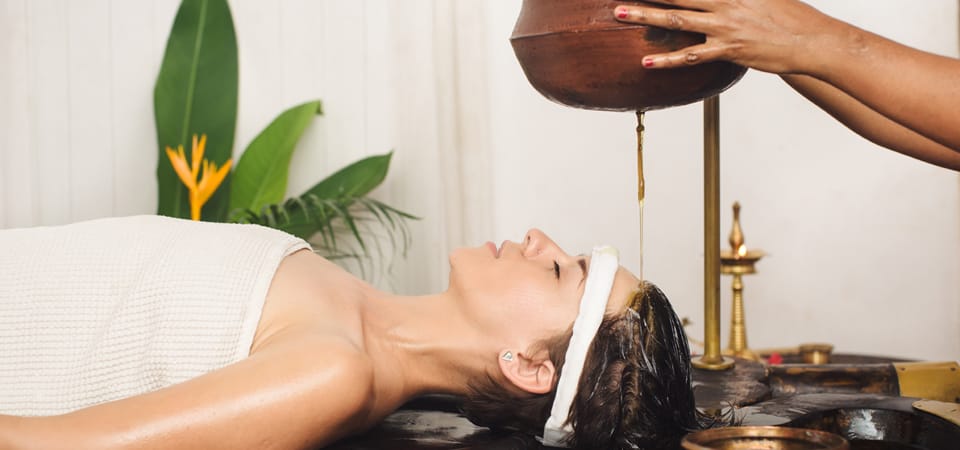

Panchakarma
Panchakarma is an elegant cleansing process that releases stored toxins and restores the body's innate healing ability.
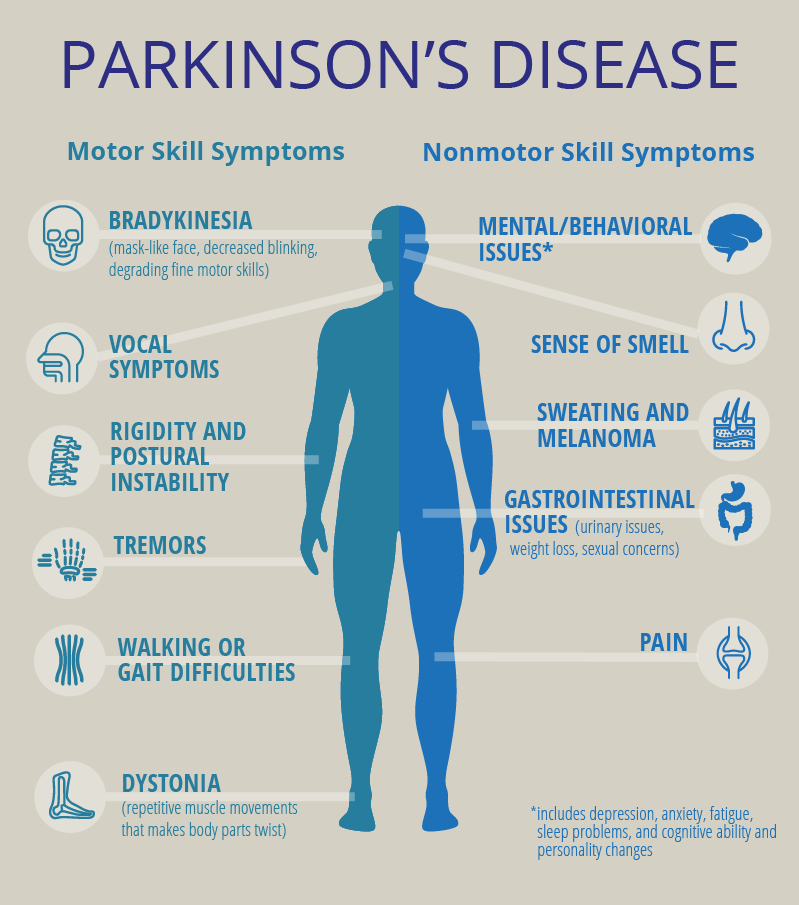
Parkinson disease
Parkinson's disease affects the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine.

Pediatric & Child Care
Pediatricians are specially educated and trained in diagnosing and treating illnesses in infants, children and adolescents.
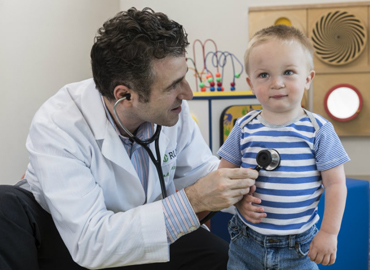
Pediatric Cardiology
Pediatric cardiologists diagnose, treat, and manage heart problems in children, including “Congenital heart disease” (heart differences children are born with), such as holes between chambers of the heart, valve problems, and abnormal blood vessels “Arrhythmias”, or abnormal heart rhythms caused by the electrical system that controls the heart beat.